Python(3.6) is an object oriented programming language,everything in Python is an object.Unlike procedure oriented programming, where the main emphasis is on functions, object oriented programming stress on objects.
Object is simply a collection of data (variables) and methods (functions) that act on those data.
Class variable − A variable that is shared by all instances of a class. Class variables are defined within a class but outside any of the class's methods. Class variables are not used as frequently as instance variables are.
Data member − A class variable or instance variable that holds data associated with a class and its objects.
Instance variable − A variable that is defined inside a method and belongs only to the current instance of a class.
Instance − An individual object of a certain class. An object obj that belongs to a class Circle, for example, is an instance of the class Circle.
Instantiation − The creation of an instance of a class.
create class:classes are defined by the "Class" keyword
class classname():
variables;
to declare functions in python using "def" keyword followed by function name.
def functioname():
# declare varables and functions in class below sample example
create instance of class: objectname=classname()
you can call mehtod/s using objectname.methodname().
create instance of class: objectname=classname()
you can call mehtod/s using objectname.methodname().
The Constructor Method:
The constructor method is used to initialize data. It is run as soon as an object of a class is instantiated. Also known as the
__init__ method, it will be the first definition of a class and looks like this: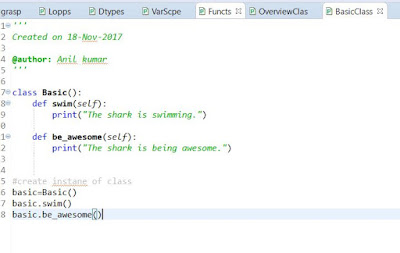

No comments:
Post a Comment